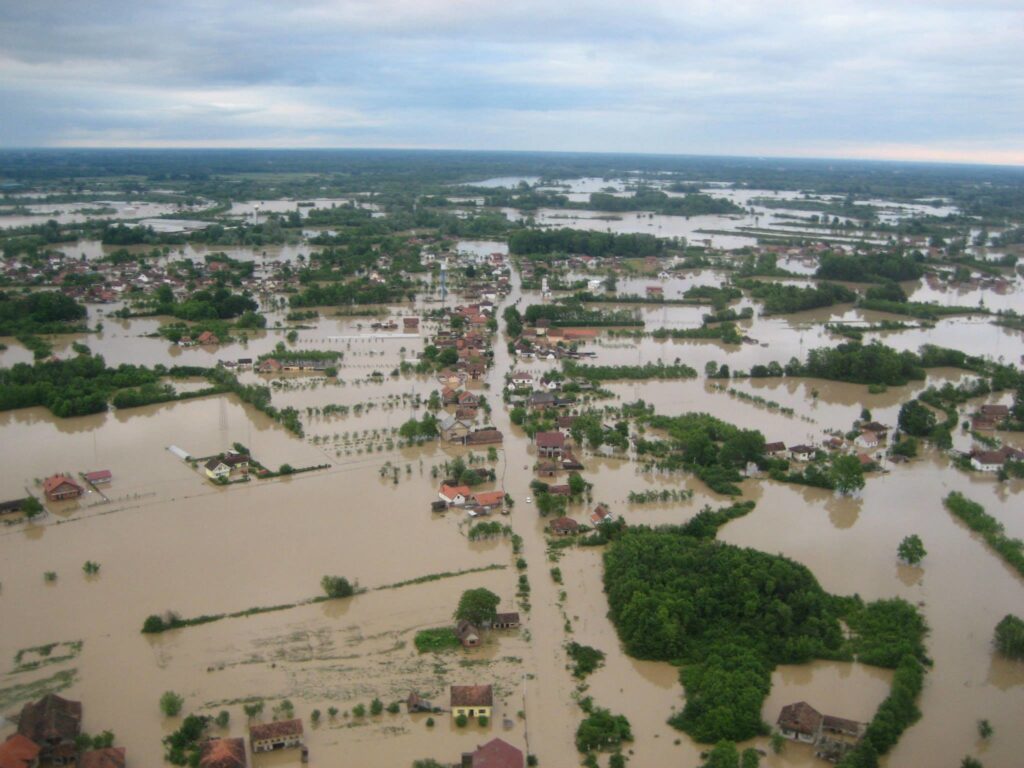
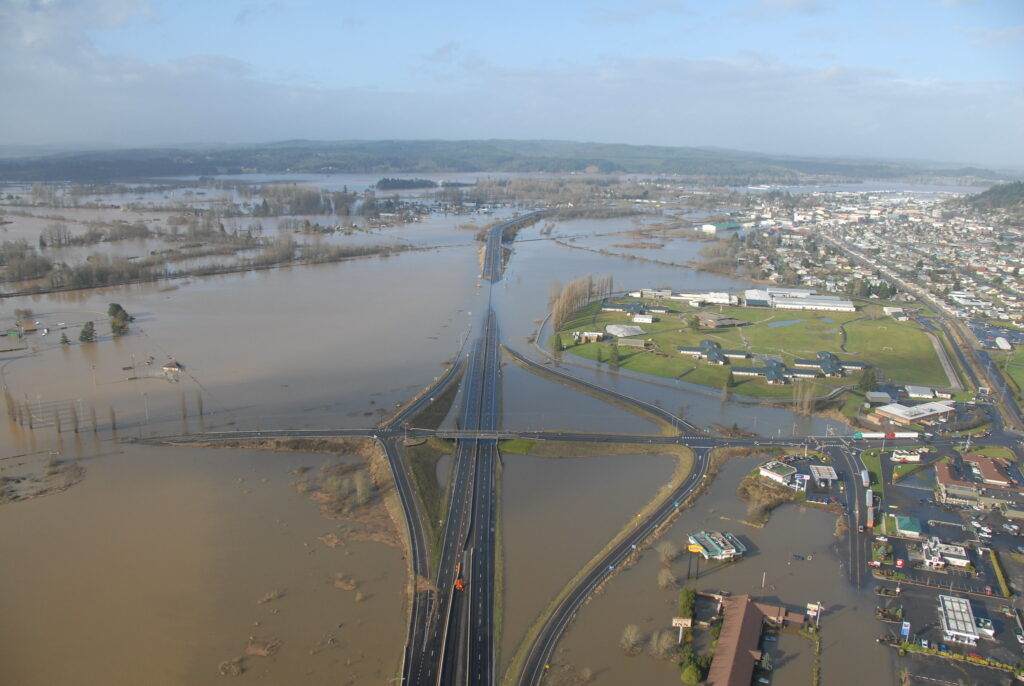
Floods are devastating natural disasters that can strike anywhere at any time. Because of their potential impact on communities, infrastructure and ecosystems, it is crucial to adopt effective prevention strategies and to manage crises proactively. This article explores best practice in preparing for floods, as well as the essential steps for effective crisis management.
Understanding Flood Risks
Before drawing up a prevention plan, it is important to understand the different types of flooding and the associated risks. Floods can be caused by torrential rainfall, rising water levels, storms or breaches of dykes. Each type of flood presents unique preparedness and management challenges.
Types of Flooding
Fluvial flooding: caused by major flooding in rivers and streams.
Urban flooding: caused by intense rainfall that exceeds the capacity of drainage systems.
Coastal flooding: resulting from storms, storm surges or tsunamis.
Flood Prevention Strategies
Prevention is the first line of defence against flooding. Here are some key strategies to minimise risk and protect your property:
Risk Assessment
Carrying out a risk assessment helps to identify the specific vulnerabilities of your property and region. This assessment should include:
Flood history analysis: review past flood data.
Flood mapping: using maps to identify areas of high risk.
Infrastructure inspection: assess the condition of drainage systems and flood barriers.
Land-use planning
Spatial planning plays a crucial role in flood prevention:
Urban planning: avoid building in flood-prone areas.
Rainwater management: installing efficient drainage systems and rainwater storage reservoirs.
Reforestation: plant trees to reduce runoff and stabilise the soil.
Self-protection measures
Homeowners can also take steps to protect their homes from flooding:
- Installation of barriers: use sandbags, flood walls and removable barriers.
- Elevating assets: elevate water-sensitive equipment and materials.
- Warning systems: install water sensors and warning systems to receive notifications of rising water.
Flood crisis management
In the event of a crisis, effective management is essential to minimise damage and ensure people’s safety. Here are the key steps to effective management:
Emergency Response Planning
Having an emergency response plan is crucial:
- Drawing up an evacuation plan: defining safe routes and assembly points.
- Staff training: train community members and employees on evacuation procedures and safety measures.
- Communicating alerts: setting up communication systems to disseminate flood alerts and information.
Rescue coordination
Coordination between local authorities, relief teams and humanitarian organisations is essential:
- Resource management: allocating resources such as relief teams and supplies efficiently.
- Disaster support: providing temporary shelter, medical care and support resources to those affected.
- Damage assessment: inspecting damage and assessing repair and assistance needs.
Post-flood rehabilitation
After a flood, it’s important to focus on rehabilitation:
- Clean-up and repair: clearing debris and repairing damage to infrastructure and property.
- Impact assessment: analysing environmental and social impacts to better prepare for future crises.
- Building resilience: implementing improvements based on lessons learned to build resilience to future flooding.
Conclusion
Effective flood crisis preparedness and management is essential to protect lives and property. By implementing robust prevention strategies and developing emergency response plans, you can reduce risk and improve your community’s resilience to flooding.
Adopt these measures today to prepare for flooding and ensure effective disaster management.